12. March 2025 By Kevin Ludwig and Matthias Zurth
Life Sciences: Innovation and compliance with SAP BTP governance in line
SAP is and remains the leading standard in the life sciences industry – particularly visible in the current transformation towards S/4HANA. In this context, SAP Business Technology Platform (SAP BTP) is becoming increasingly important. As a central platform for integration, development and the use of artificial intelligence (AI), SAP BTP enables the linking of complex system landscapes, the development of innovative applications and the evaluation of large amounts of data using AI-supported analyses.
However, the versatility of the platform also entails risks: without clear governance and standardisation, there is a risk of shadow IT, inefficiency, high costs and a lack of GxP compliance. To avoid these pitfalls, a well-thought-out BTP governance is required. In this blog post, I will show you how companies in the life sciences industry establish effective BTP governance to ensure innovation, efficiency and GxP compliance.
What is BTP governance and what are the key elements of effective SAP BTP governance?
BTP governance is the backbone of a successful BTP implementation. It defines the strategic framework, sets guidelines and monitors compliance. It ensures that all developments are secure, compliant and cost-controlled.
Effective BTP governance is based on several essential building blocks that together create a stable foundation for security, efficiency and innovation. First, a clear strategy with binding guidelines is crucial. This includes specific requirements for the use of BTP services, defines architecture standards and sets security guidelines. This ensures that all developments and integrations follow a consistent framework. Another key component is security and compliance. Standardised access policies, comprehensive data protection concepts – for example, in accordance with GDPR standards – and regular audits protect data and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Efficient cost management is essential to avoid budget overruns. This is supported by clear budget guidelines, continuous cost monitoring and a proactive alerting system that points out deviations. Standardised application development is ensured by well-thought-out service and API management, which defines guidelines for interfaces and establishes central administration of APIs. This avoids redundancies and increases the reusability of services. Another pillar is architecture governance, which ensures that new projects are subject to a defined review process. This guarantees technical quality and ensures that architecture standards remain consistent. Finally, clearly defined roles and responsibilities are essential. Assigning roles such as BTP owner, service manager and architects creates transparency and ensures that all tasks are efficiently coordinated.

Components of SAP BTP Governance
Together, these building blocks provide the foundation for effective BTP governance. They minimise risk, keep costs under control and enable life sciences companies to implement innovations in a safe and sustainable way.
Maximise your SAP potential with the SAP Business Technology Platform
Innovative, secure, efficient – with the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP), you can shape the future of your company. Whether it's integration, automation or AI-supported analysis, we can help you get the most out of SAP BTP and transform your business processes.
How is BTP governance implemented and integrated into existing corporate structures?
A structured introduction of BTP governance is crucial for its sustainable success. It ensures that processes are implemented consistently and continuously optimised. The introduction takes place in several clearly defined phases:
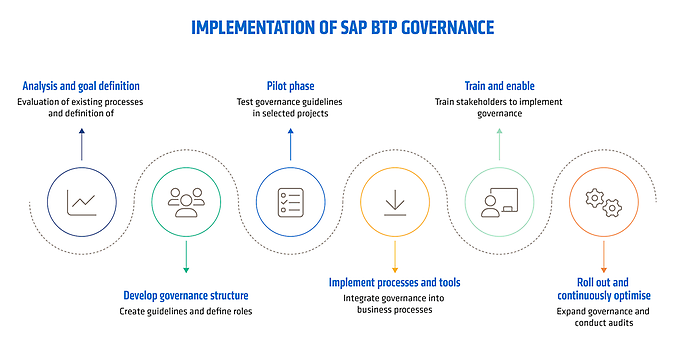
Implementation of SAP BTP Governance
- 1. Analysis and goal definition: in the first phase, the existing processes, IT landscapes and requirements are recorded. Gaps are identified through interviews with stakeholders and a detailed inventory. At the same time, clear goals for governance are defined, for example, cost control, risk minimisation or standardisation.
- 2. Develop governance structure: Based on the results of the analysis, governance guidelines are created and roles and responsibilities are defined. This includes setting up a governance board that monitors compliance with the guidelines and centrally controls decisions.
- 3. Pilot phase: The developed governance concepts are tested in selected projects. This phase serves as a test run to check the effectiveness of the guidelines and to collect feedback from practical experience at an early stage. Any potential for improvement is integrated into the guidelines.
- 4. Implement processes and tools: After a successful pilot, governance is integrated into business processes. This includes implementing monitoring and reporting tools, as well as adapting existing processes to the new requirements. Automated dashboards help to quickly identify deviations.
- 5. Training and enablement: To ensure that governance is successfully embedded, it is essential to train all relevant stakeholders. Training programmes, workshops and guidelines provide employees with the knowledge they need to implement governance guidelines in their daily work.
- 6. Rollout and continuous optimisation: Governance is rolled out across the company. At the same time, regular reviews and audits are carried out to verify compliance. Continuous monitoring and feedback collection help to further develop and improve governance on an ongoing basis.
This step-by-step introduction ensures that BTP governance is not only designed, but also successfully implemented in day-to-day business in the long term.
What role does a BTP Center of Excellence (CoE) play?
In most cases, the overarching goal is to establish a Center of Excellence (CoE) for SAP BTP in order to exploit the possibilities and potential of SAP BTP and to establish a future-proof SAP landscape. It is the operational hub for the successful use of SAP BTP. It ensures that the defined governance requirements are implemented in a practical way and continuously developed. The CoE acts as a bridge between strategy and operational implementation.
The main tasks of a BTP CoE:
- Consolidating knowledge and establishing best practices: Developing and providing standardised frameworks, templates and guidelines for BTP use.
- Supporting development teams: Training, coaching and technical support to promote consistent implementation.
- Drive innovation: Initiate proof of concepts (PoCs) and pilot projects to test new BTP services.
- Implement governance requirements operationally: Conduct architecture reviews, quality assurance and compliance with security standards.
- Promote community and exchange: Develop knowledge sharing platforms, communities of practice and internal forums.

Core tasks of a BTP COE
Conclusion: SAP BTP governance and CoE in life sciences
Well-thought-out SAP BTP governance is essential to successfully balancing innovation, efficiency and regulatory compliance in the life sciences industry. It creates the strategic framework for security, standardisation and cost control. At the same time, a strong centre of excellence ensures that these requirements are implemented operationally and continuously developed. Together, governance and the CoE form the basis for the successful use of SAP BTP, promote innovation and ensure that companies always meet industry regulatory requirements.
We support you!
Do you want to optimise your SAP BTP governance and develop a future-proof strategy for your company? Our experts will help you establish the right structures and processes – efficiently, in compliance with regulations and innovatively.


