27. November 2024 By Libero Raspa
Current Areas of Application of AI in the Banking Sector
The use of Artificial Intelligence enables banks to achieve innovative approaches and efficiency improvements in various areas such as customer service or risk management. To develop meaningful and high-quality AI models, a sufficiently large amount of data and suitable data quality are necessary as technological prerequisites. The list of possibilities that can arise from this data is extensive. It ranges from detecting fraudulent activities in credit card transactions to KYC processes (Know Your Customer) and uncovering cyber-attacks, as well as automated loan approvals.
Customer-oriented applications in the front office
The current focus of the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in banks lies in customer-oriented front-office applications, process-oriented back-office systems, and regulatory processes.
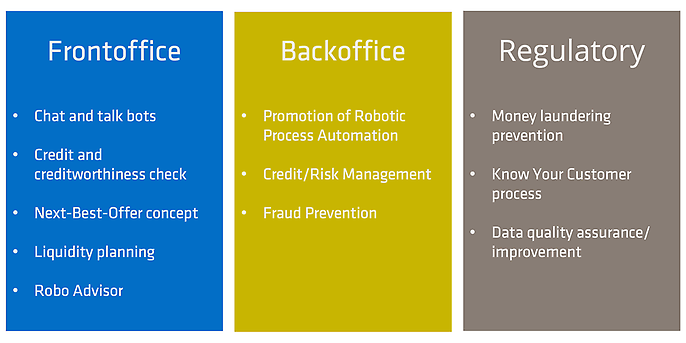
Current Areas of Application of Artificial Intelligence in Banking, Source: Own Representation, based on Kaya (2018)
Chatbots and voice assistants in banking
In the competition for direct customer contact, those banks or service providers are likely to be successful that can offer the best customer experience. AI solutions promise various improvements such as round-the-clock availability, enabling the use of chatbots or voice assistants. In 2017, Comdirect became the first German bank to introduce a skill for Amazon's voice assistant Alexa, which allows users to access stock market news and real-time price information. Additional features such as transferring funds via voice control have also been introduced.
AI-powered digital assistants for credit processes
Chatbots and voice assistants are only considered intelligent when they are able to recognise, structure, and apply meaningful question-answer relationships beyond predefined if-then scenarios. In Germany, for example, a digital assistant for online consumer credit applications is still in the experimental phase. A chatbot or voice assistant is only perceived as intelligent or positive if it can provide helpful and correct answers to individual and complex questions. Otherwise, there is a risk of an extremely negative customer experience.
In the retail banking sector as well as in the already largely automated lending business, there are further application possibilities for artificial intelligence (AI). In particular, house banks can benefit from implemented AI solutions, for example, to secure or improve data quality and to utilise extensive transaction data. The use of AI can simplify the determination of creditworthiness for both the bank and the customer. For financing inquiries or before signing a lease agreement, banks or landlords usually require a "Confidential Self-Disclosure". There is a solution with integrated AI for this process, which automatically derives and structures desired information from existing transaction data. This eliminates certain steps such as submitting salary statements. An automatically filled out self-disclosure reduces the effort for interested parties and accelerates the decision-making process up to the credit decision. In addition, the bank saves manual steps in reading and checking the already available information and can optimize the risk assessment by considering all known data.
Furthermore, the banking industry offers potential for automated data analysis to identify and address individual customer needs. By using product recommendations based on the successful “Next Best Offer” concept, additional business opportunities can be created. By using machine learning, previously undiscovered interactions can be identified to improve both the quality of recommendations and the conversion rate.
Banks can also use AI and machine learning at the customer interface in corporate banking, for example, in liquidity planning. Some banks have developed the so called “CashRadar” for this purpose. Historical account data is analysed using machine learning to create a forecast of future balances for the next four months. This can warn against potential shortfalls and reduce the risk for customers.
Automation for back-office efficiency
In the back-office systems of banks, most current use cases of artificial intelligence aim to increase automation levels to enhance efficiency. Numerous solutions of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) are already being used, which mimic human processes. AI technologies have the potential to further expand RPA by processing previously unstructured inputs. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) can recognize texts and images, while Natural Language Processing (NLP) can understand and evaluate them. In this way, scanned documents, salary statements, identification documents, and other application and contract documents can be categorised for further processing by RPA applications.
Another focus of current AI development is the improvement of operational risk management. FinTechs already offer AI-supported solutions to prevent fraud in payment transactions. Payment instructions via credit cards or online banking are checked in real-time for plausibility by comparing the recipient, amount, and location with historical transaction data. If the AI detects significant deviations or other risks, the payment can be blocked, and an audit order can be created for a bank employee.
Regulatory processes
The use of AI also offers potential to increase efficiency and quality in meeting regulatory requirements.
AI against money laundering
A concrete example is anti-money laundering. Banks are legally obliged to check all payment transactions for suspicious transactions and report them to the relevant authorities. There are already automated verification procedures to prevent money laundering, which are based on predefined detection rules defined by experts. However, some of these rules only refer to individual characteristics of transactions, which can also occur in many harmless payments. As a result, many suspicious cases are reported, which have to be rejected in a subsequent manual review. At the same time, there is a risk of systematically circumventing these rules by deliberately falling below known thresholds, for example, or using other methodologies. For this reason, various banks are testing machine learning approaches for continuous feedback on current detection rules and for deriving new, previously unknown detection patterns. With the help of AI, the number of unfounded suspicious cases and the manual effort can be reduced, while previously hidden money laundering cases can be uncovered.
Optimisation of the KYC process
Furthermore, AI applications can support the “Know Your Customer” process. In order to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing and to comply with applicable sanctions, banks must continuously verify the data of their customers for accuracy and correctness. There are already AI applications that generally check reported or guided customer data for plausibility and, if necessary, compare it with information from the internet. If obviously outdated data such as postal codes with four digits or information contradicting publicly available media is found, an employee is involved for individual verification. In a further stage of development, automated correction of incorrect data or supplementation of missing data is also possible.
GenAI in banking: shaping the future, starting today
How can banks and financial service providers make meaningful use of generative AI? Discover innovative applications that make processes more efficient, improve the customer experience and secure competitive advantage. Learn more about the opportunities and challenges of GenAI and how you can use this technology strategically. Start your journey into the future of finance with adesso as your strong partner.

